7 Lessons From The Helicopter Crash Investigation
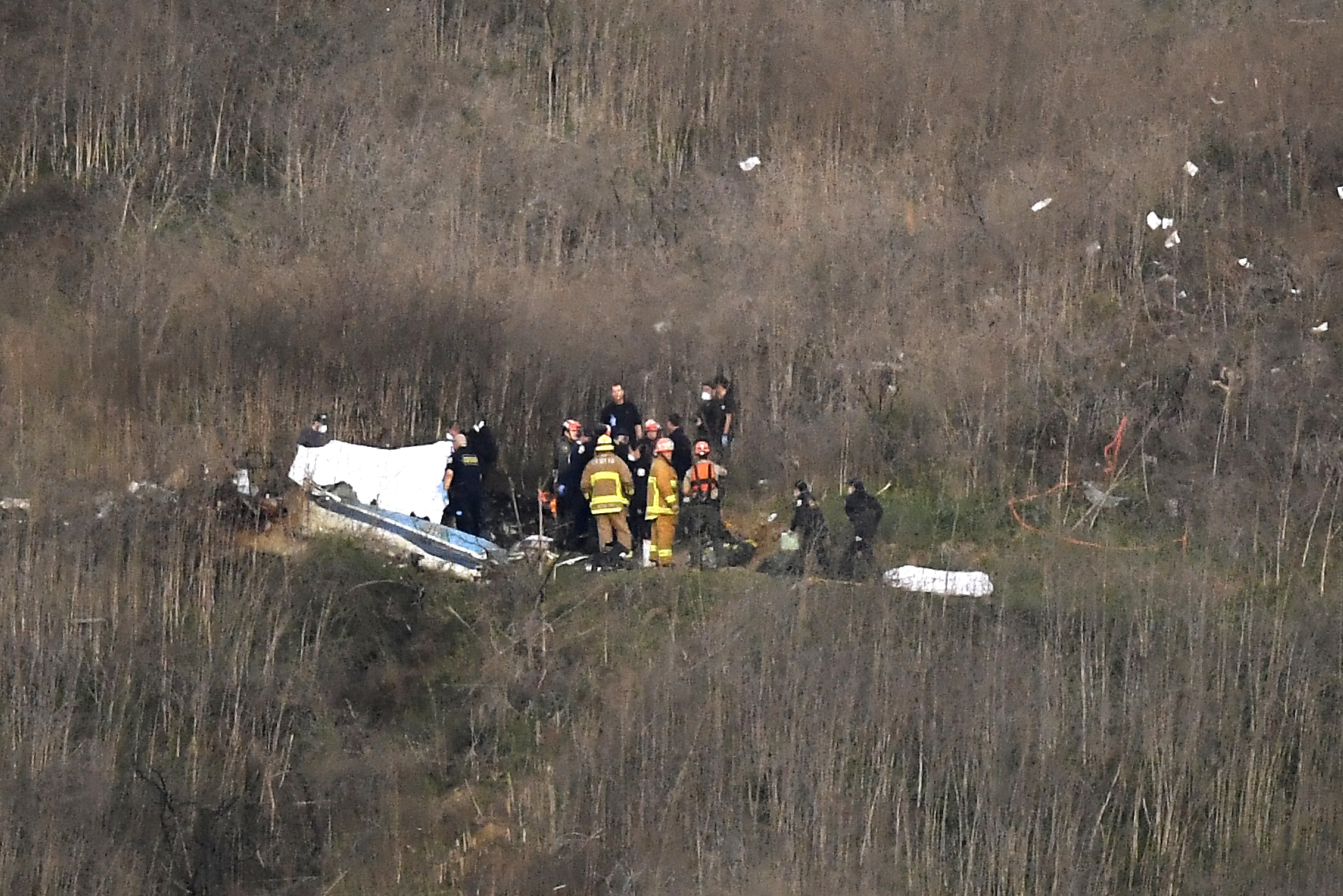

The helicopter crash that claimed the lives of nine people, including basketball legend Kobe Bryant, his daughter Gianna, and seven others, sent shockwaves around the world. As the investigation into the crash continues to unfold, several key lessons have emerged that can help inform and improve helicopter safety. In this article, we will delve into the details of the crash, the subsequent investigation, and the critical takeaways that can be applied to the aviation industry as a whole. The National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) has been at the forefront of the investigation, and their findings have shed light on the importance of aviation safety protocols, pilot training, and weather conditions.
Introduction to Helicopter Crash Investigations

Helicopter crash investigations are complex and multifaceted, involving a range of factors including human error, mechanical failure, and environmental conditions. In the case of the Kobe Bryant helicopter crash, the NTSB has been working to determine the probable cause of the accident, which occurred on a foggy morning in Calabasas, California. The investigation has involved a thorough analysis of the helicopter’s maintenance records, pilot experience, and weather conditions at the time of the crash. As we examine the lessons from this investigation, it is essential to consider the interplay between these factors and how they can impact the safety of helicopter operations.
Lesson 1: The Importance of Weather Briefings
The investigation has highlighted the critical importance of weather briefings for pilots. On the morning of the crash, the pilot, Ara Zobayan, was flying under visual flight rules (VFR), which require pilots to navigate visually and avoid flying into clouds or other obscuring conditions. However, the weather conditions were deteriorating, with low visibility and low ceilings reported in the area. The NTSB has emphasized the need for pilots to obtain accurate and up-to-date weather briefings before embarking on a flight, particularly in areas with rapidly changing weather conditions. This is especially relevant for instrument flight rules (IFR) flights, which require pilots to navigate using instruments rather than visual references.
| Weather Condition | Visibility |
|---|---|
| Low Visibility | 1-3 miles |
| Low Ceilings | 1,000-2,000 feet |

Lesson 2: The Need for Enhanced Pilot Training
The investigation has also highlighted the need for enhanced pilot training, particularly in the area of instrument meteorological conditions (IMC). The pilot, Ara Zobayan, was certified to fly under IFR, but the NTSB has raised questions about his experience and training in IMC conditions. The agency has emphasized the importance of providing pilots with regular and comprehensive training in IMC conditions, as well as scenario-based training to prepare them for unexpected weather events. This type of training can help pilots develop the skills and confidence needed to navigate complex weather situations.
Lesson 3: The Role of Air Traffic Control
The investigation has also examined the role of air traffic control in the crash. The NTSB has raised questions about the level of air traffic control services provided to the pilot, particularly in the moments leading up to the crash. The agency has emphasized the importance of providing clear and concise communication between air traffic controllers and pilots, as well as effective traffic management to prevent conflicts between aircraft. This is especially critical in areas with high volumes of air traffic, where the risk of collisions or other safety incidents is increased.
Technical Specifications and Performance Analysis

The helicopter involved in the crash was a Sikorsky S-76B, a widely used aircraft in the executive transport and emergency medical services (EMS) sectors. The investigation has examined the technical specifications of the aircraft, including its performance capabilities and system redundancies. The NTSB has also analyzed the aircraft’s maintenance records, which showed that it had been properly maintained and inspected in accordance with regulatory requirements. However, the agency has raised questions about the adequacy of the aircraft’s design and certification standards, particularly in relation to its performance in IMC conditions.
Lesson 4: The Importance of Maintenance and Inspection
The investigation has highlighted the critical importance of maintenance and inspection in ensuring the safety of helicopter operations. The NTSB has emphasized the need for regular and comprehensive maintenance checks, as well as robust inspection protocols to identify potential safety issues before they become major problems. This includes the use of non-destructive testing (NDT) techniques, such as X-ray and ultrasound, to detect cracks or other defects in critical components.
| Maintenance Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| 100-hour inspection | Every 100 hours of flight time |
| Annual inspection | Every 12 months |
Lesson 5: The Need for Enhanced Safety Protocols
The investigation has also highlighted the need for enhanced safety protocols in helicopter operations, particularly in the area of risk management. The NTSB has emphasized the importance of hazard identification and mitigation, as well as crew resource management (CRM) to improve communication and decision-making among pilots and other crew members. This includes the use of safety management systems (SMS) to identify and mitigate potential safety risks, as well as regular safety audits to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Lesson 6: The Role of Technology in Helicopter Safety
The investigation has also examined the role of technology in improving helicopter safety, particularly in the area of aviation safety equipment. The NTSB has highlighted the importance of advanced avionics systems, such as terrain awareness and warning systems (TAWS) and synthetic vision systems (SVS), in enhancing pilot situational awareness and reducing the risk of accidents. This includes the use of automatic dependent surveillance-broadcast (ADS-B) systems, which provide real-time position and velocity information to air traffic controllers and other aircraft.
Lesson 7: The Importance of Regulatory Oversight
Finally, the investigation has highlighted the importance of regulatory oversight in ensuring the safety of helicopter operations. The NTSB has emphasized the need for robust regulatory frameworks and effective enforcement mechanisms to prevent accidents and protect the public. This includes the use of regulatory audits and inspections to ensure compliance with safety standards, as well as penalties and fines for non-compliance.
What is the current state of helicopter safety in the United States?
+The current state of helicopter safety in the United States is a complex and multifaceted issue, with a range of factors contributing to the risk of accidents. According to the NTSB, the helicopter accident rate has been declining in recent years, with a total of 122 accidents reported in 2020, resulting in 17 fatalities. However, the agency has emphasized the need for continued vigilance and improvement in areas such as pilot training, maintenance, and regulatory oversight.
What can be done to improve helicopter safety in the future?
+To improve helicopter safety in the future, a range of measures can be taken, including enhanced pilot training, improved maintenance and inspection protocols, and the adoption of advanced safety technologies such as TAWS and SVS. Additionally, regulatory oversight and enforcement mechanisms can be strengthened to prevent accidents and protect the public