Tempest Fighter Jet Vs F-35
The world of military aviation is witnessing a significant shift with the introduction of next-generation fighter jets, designed to dominate the skies for decades to come. Two of the most talked-about aircraft in this category are the Tempest fighter jet, a sixth-generation fighter being developed by the United Kingdom, Italy, and Sweden, and the F-35 Lightning II, a fifth-generation multirole fighter developed by the United States in collaboration with several other countries. Both aircraft represent the pinnacle of modern aerospace technology, but they have distinct design philosophies, capabilities, and intended roles. This article will delve into the specifics of each aircraft, comparing their designs, capabilities, and the implications of their development for the future of military aviation.
Introduction to the Tempest and F-35

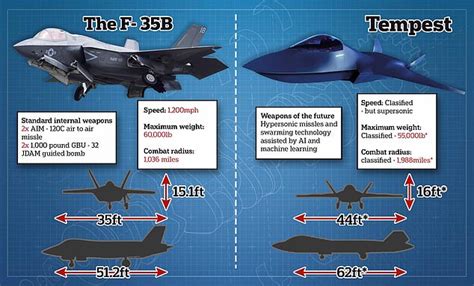
The Tempest and the F-35 are both highly advanced fighter jets, but they were conceived with different priorities and operational environments in mind. The F-35, already in service with several countries, is designed to be a multirole fighter capable of performing a variety of tasks, including air-to-air combat, air-to-ground strikes, and reconnaissance. It features stealth technology, advanced avionics, and a highly integrated computer system that allows for real-time data sharing and coordination with other assets. On the other hand, the Tempest, still in development, is envisioned as a sixth-generation fighter that will incorporate even more advanced technologies, including artificial intelligence (AI), directed energy weapons, and potentially, unmanned teaming capabilities. The Tempest is designed to be highly adaptable, with an open architecture that allows for easier integration of new technologies and systems as they become available.
Design and Capabilities
The design of the Tempest and F-35 reflects their different generations and design philosophies. The F-35, with its stealth capabilities, is shaped to minimize its radar cross-section, making it harder to detect. It also features a single engine and is designed to be versatile, with three main variants: the F-35A for conventional takeoff and landing, the F-35B for short takeoff and vertical landing, and the F-35C for carrier-based operations. The Tempest, on the other hand, is expected to push the boundaries of fighter jet design further, with concepts including a modular design that could allow for the easy swapping of different mission systems, advanced materials and manufacturing techniques to reduce weight and increase durability, and potentially, hypersonic capabilities. The Tempest’s design also prioritizes sustainability and maintainability, aiming to reduce the logistical footprint and increase the availability of the aircraft for missions.
| Aircraft | Generation | Stealth Capability | Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| F-35 | Fifth | Yes | Multirole |
| Tempest | Sixth | Expected | Multirole with Advanced Technologies |

Technical Specifications and Performance

Comparing the technical specifications of the Tempest and F-35 provides insight into their performance capabilities. The F-35, powered by a single Pratt & Whitney F135 engine, has a top speed of over Mach 1.6 and a range of more than 1,200 nautical miles. The Tempest, with its planned advanced engine and potentially hybrid-electric propulsion, is expected to offer superior performance, including increased speed, range, and maneuverability. The Tempest’s performance will also be enhanced by its advanced aerodynamic design and the integration of advanced materials that can withstand higher temperatures and stresses.
Future Implications
The development and deployment of the Tempest and continued evolution of the F-35 have significant implications for the future of military aviation. These aircraft, with their advanced technologies and capabilities, are not just weapons systems but platforms for integrating a wide range of military assets and systems. They represent a shift towards more networked warfare, where the aircraft is a node in a larger network of sensors, command centers, and other assets, all working together in real-time. The Tempest, in particular, with its focus on adaptability and sustainability, signals a move towards a more flexible and efficient approach to military aviation, where aircraft can be easily upgraded and adapted to new roles and technologies as they emerge.
The introduction of these advanced fighters also raises questions about the future of airpower and the balance of military capabilities among nations. As more countries develop or acquire advanced fighter jets, the global landscape of air superiority will evolve, potentially leading to new alliances, strategies, and technologies aimed at countering these capabilities. The race to develop and deploy the most advanced fighter jets is, therefore, not just about fielding a superior weapon system but about shaping the future of military strategy and international relations.
What are the primary differences between the Tempest and F-35 fighter jets?
+The primary differences lie in their design generation, capabilities, and intended roles. The F-35 is a fifth-generation multirole fighter with stealth capabilities, while the Tempest is a sixth-generation fighter designed to incorporate advanced technologies such as AI, directed energy weapons, and potentially, unmanned teaming capabilities.
How do the performance capabilities of the Tempest and F-35 compare?
+The Tempest, with its planned advanced engine and potentially hybrid-electric propulsion, is expected to offer superior performance, including increased speed, range, and maneuverability compared to the F-35. However, exact specifications for the Tempest are still in development and subject to change.
What are the implications of the Tempest and F-35 for the future of military aviation?
+These aircraft represent a shift towards more networked and adaptable forms of warfare, with a focus on integrating advanced technologies and systems. They signal a future where airpower is more flexible, sustainable, and closely integrated with other military assets and systems.
In conclusion, the Tempest and F-35 are at the forefront of modern military aviation, representing the current pinnacle of fighter jet technology and design. As these aircraft continue to evolve and enter service, they will play significant roles in shaping the future of air warfare, military strategy, and international relations. Understanding their capabilities, implications, and the technologies they embody is crucial for appreciating the trajectory of military aviation and the broader geopolitical landscape.



